Welcome to imalshablog.blogspot.com. In my first blog, I decided to write about the stack data structure. It is a very easy and basic data structure as well as it is a linear data structure.
A stack is a list of elements in which an element may be inserted or deleted only at one end, called the top of the stack.
The insertion or deletion is happened according to the LIFO principle. LIFO stands for Last-In-First-Out.
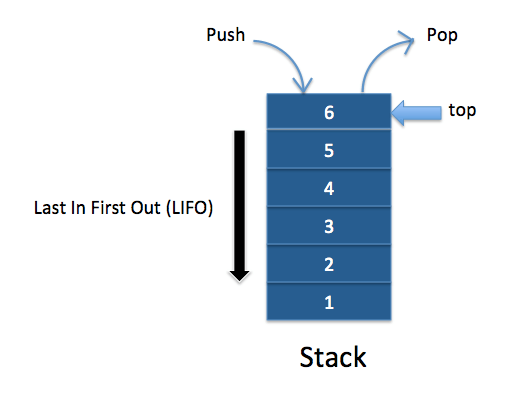
Mainly, there are five basic operations have in the stack.
A stack is a list of elements in which an element may be inserted or deleted only at one end, called the top of the stack.
The insertion or deletion is happened according to the LIFO principle. LIFO stands for Last-In-First-Out.

Mainly, there are five basic operations have in the stack.
- Push -: This operation is used for inserting an element in the stack.
Before happening push operation, check whether the stack is full. if the stack is full, display the error message and exit. if the stack is not full, increment top to point next empty space and inserts the next element to stack top.
Push Algorithm
IF top = max - 1
print overflow
END IF
SET top = top + 1
SET stack[top] = value
END
- Pop -: This operation is used for removing an element from the stack.
Before performing the pop operation, we check whether the stack is empty. if the stack is empty, exit from the process. Then, it means the stack is empty and no more deletions can be done.
Otherwise, the element of the stack top that can be deleted. But, this element is not actually removed.
Pop Algorithm
IF top = null
print underflow
END IF
SET Value = stack[top]
SET top = top - 1
END
- Top or Peek -: top or peek is an operation that returns the value of the topmost element of the stack without deleting it from the stack.
Peek Algorithm
IF top = null
print stack is empty
ENDIF
Return stack[top]
END
- isEmpty -: Return true if the stack is empty. otherwise, return false
- isFull -: Return true is the stack is full. otherwise, return false
The following example provided for stack data structure.
#include<stdio.h>
#define MAX 100
#define MAX 100
int stack[MAX];
void push(int);
void pop();
int peek();
int display();
int top =-1;
int i;
void push(int);
void pop();
int peek();
int display();
int top =-1;
int i;
void push(int x){
if(top==MAX-1){
printf("stack overflow");
}else{
top++;
if(top==MAX-1){
printf("stack overflow");
}else{
top++;
stack[top]=x;
}
}
}
}
void pop(){
if(top==-1){
printf("stack underflow");
}else{
stack[top--];
}
}
if(top==-1){
printf("stack underflow");
}else{
stack[top--];
}
}
int peek(){
if(top==-1){
return 0;
if(top==-1){
return 0;
}else{
return stack[top];
}
}
return stack[top];
}
}
int display(){
if(top==-1){
printf("stack is underflow");
}else{
for(i=top;i>=0;i--){
printf("\n %d",stack[i]);
printf("\n");
}
}
}
int main(){
int x,option,i;
do{
printf("\n ***MAIN MENU****");
printf("\n 1. push");
printf("\n 2. pop");
printf("\n 3. peek");
printf("\n 4. display");
printf("\n 5. exit");
printf("\n Enter the option:");
scanf("%d",&option);
switch(option){
case 1:
printf("\nEnter the push number:");
scanf("%d",&x);
push(x);
break;
case 2:
pop();
break;
case 3:
peek();
if(top!= -1);
printf("\n value:%d\n",x);
break;
case 4:
display();
break;
}
}while(option != 5);
return 0;

Comments
Post a Comment